What is Cystocele?
Cystocele is an example of when the tissues between the bladder and vaginal wall weaken causing it to apply pressure on the front vaginal wall and in some cases, drop into the vagina causing pressure on other organs. This can happen when the various muscles and ligaments surrounding the bladder weaken or stretch from childbirth, excessive straining or age. Because of the overall effect on the bladder in this circumstance, this condition has also more commonly been referred to as “dropped bladder.” It is also referred to as an anterior prolapse as the front (or anterior) vaginal wall has collapsed allowing the bladder to bulge downward into the vagina.
CYSTOCELE PROGRESSION WITH UTERUS
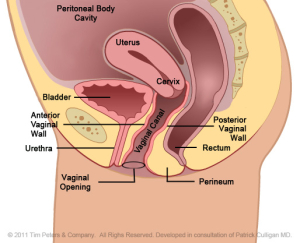
Normal Pelvic Cavity with Uterus.
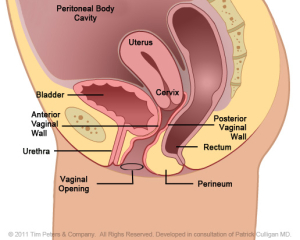
Weakening support around the vaginal wall gives way to the bladder.
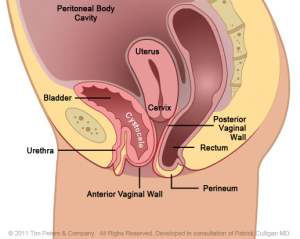
Vaginal wall giving way to the bladder effecting uterus and rectum.
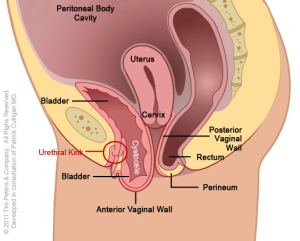
Advanced cystocele showing total collapse of support and kink in urethra.
Original Images Courtesy of BARD Medical – Subject to Copyrights. Labeling Enhanced for Educational Purposes by D. K. Veronikis, MD
The image on the far left reflects the normal position of the Anterior Vaginal Wall and of the bladder. Moving from left to right, the image on the far right shows an advanced case of anterior vaginal wall prolapse with the uterus in place. Additionally, the advanced prolapse of the anterior vaginal wall has obstructed the urethra which may cause challenges with obstructed urination or symptoms of Incontinence. With advancing prolapse (as indicated on the far right) the bladder will protrude thru the vaginal opening and will be perceived as a bulge. Singular pelvic floor defects are a rare occurrence. For the benefit of explanation we will consider Cystocele in isolation. A Cystocele is a defect of the support of the anterior vaginal wall and is part of Utero-Vaginal Prolapse.
CYSTOCELE PROGRESSION WITHOUT UTERUS
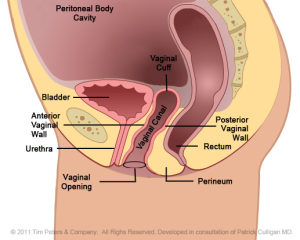
Pelvic cavity post-hysterectomy – without uterus.
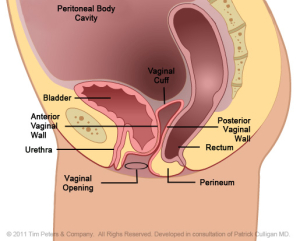
Weakening support around the vaginal wall gives way to the bladder.
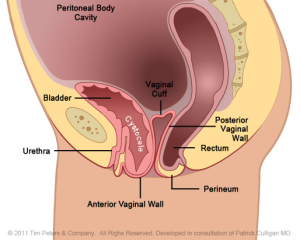
Vaginal wall giving way to the bladder effecting uterus and rectum.
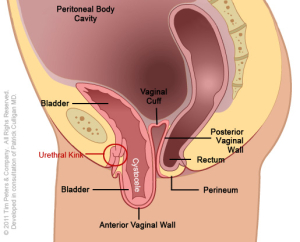
Advanced cystocele showing total collapse of support and kink in urethra.
Original Images Courtesy of BARD Medical – Subject to Copyrights Labeling Enhanced for Educational Purposes by D. K. Veronikis, MD
The image on the far left reflects the normal position of the anterior vaginal wall and of the bladder. Moving from left to right, the image on the far rights hows an advanced case of anterior vaginal wall prolapse. Additionally, the advanced prolapse of the anterior vaginal wall has obstructed the urethra which may cause challenges with obstructed urination or symptoms of Incontinence. With advancing prolapse (as indicated on the far right) the bladder will protrude thru the vaginal opening and will be perceived as a bulge. Singular pelvic floor defects are a rare occurrence. For the benefit of explanation we will consider cystocele in isolation. A cystocele is a defect of the support of the anterior vaginal wall and is a type of Vaginal Prolapse.
Symptoms of Cystocele
Because of the strain on the bladder more common symptoms relate to urinary troubles including loss of urinary control when coughing, laughing or sneezing (also known as stress incontinence), or a feeling that you haven’t completely emptied your bladder after urinating. You may also experience frequent bladder infections. Because of the shift in the organs, you may also notice a feeling of pressure in your pelvis or vagina. This can also be identified by a discomfort when your strain, cough, bear down, lift or have intercourse. In more severe circumstances you may have a feeling of sitting on a ball or notice a bulge protruding from the vaginal opening.
Cystocele Treatment
Treatment for Cystocele really depends on the severity of the condition. More mild cases benefit from exercise that strengthens the muscle tissues. For women who have experienced menopause, estrogen therapy may be beneficial as it helps keep the pelvic muscles strong. Additional supports inserted into the vagina can also be used. When surgery is required, it normally includes a reconstructive procedure that not only puts the bladder back in place, but it will also repair damage made to surrounding organs or tissue.
