What is Rectovaginal Fistula
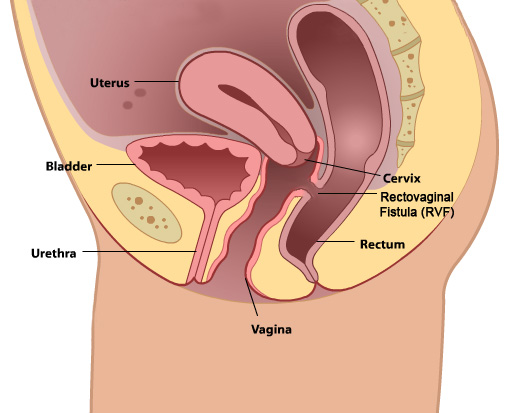
A rectovaginal fistula is an abnormal connection between the rectum and the vagina. This allows fecal material to pass freely from the rectum to the vagina.
This is not only a challenging diagnosis secondary to the medical symptoms, but the emotional impact from uncontrollable loss of stool is significant. This condition limits many women socially and functionally from activities that they would normally enjoy.
Contributing factors to rectovaginal fistula formation include prior third or fourth degree laceration during childbirth, perineal infection and impaired wound healing after childbirth, eroded pessaries, inflammatory bowel disease, particularly Crohn’s, or prior pelvic surgery.
Symptoms of Rectovaginal Fistula
The hallmark symptom of a rectovaginal fistula is the passage of stool or fecal material into the vagina. Initially this may be confused with vaginal discharge and thought to simply be secondary to a bacterial infection. A fistula may be so small it is referred to as pinpoint. It is less common to notice large amounts of stool passing into the vagina with a pinpoint fistula.
Patients may also present with dyspareunia secondary to inflammed or irritated vaginal tissue at the site of the fistula.
Again, it cannot be emphasized enough that the symptoms of a fistula have an emotional impact that is just as debilitating as the actual loss of stool itself, leading to depression and anxiety.
Evaluation of a Rectovaginal Fistula
During the office visit, the fistula is first confirmed during physical exam. In cases of very large fistulae, it may be very obvious to visualize. In smaller or pinpoint fistula, a small 1-2mm probe may be used to isolate the fistula. Many times, a coincident anal sphincter muscle injury is also present, and therefore, an ultrasound may be performed to evaluate for a defect in this muscle.
Patients who have a rectovaginal fistula secondary to Crohn’s disease may require further consultation with a medicine specialist. Additionally, patients who are suspected to have a colovaginal fistula (connection between the colon and vagina) may also benefit from further management with a colorectal specialist; this is more commonly secondary to diverticular disease.
Surgical Planning for a Rectovaginal Fistula
Once a rectovaginal fistula has been diagnosed, the next step is planning the repair. The timing of the repair can vary on the inciting event that led to the the fistula. In the setting of a broken down, infected obstetric laceration, a delayed repair may be recommended to allow for clearance of the infection and decrease in inflammation. Some patients present several months or even years after the injury and may proceed to surgery. Rarely is a colostomy required to repair rectovaginal fistulas, and a trained surgeon in repairing fistulas, such as Dr. Veronikis, are able to care for these patients. It cannot be emphasized enough that rectovaginal fistula repair should be performed by skillful surgeons who have experience and success with fistula closure.
Surgical Repair of a Rectovaginal Fistula
In our surgical philosophy of fistula repair, there two important tenets of successful closure of the defect:
- Tension-free repair to allow proper healing
- Closure of the high pressure organ (rectum)
The fistulous tract is excised, and healthy tissue is reapproximated in several layers to close the defect successfully. Any concomitant anal sphincter muscle injuries are also repaired at this primary surgery. Finally, many patients with a rectovaginal fistula will also have a defect in the perineum (muscles between the vaginal and anal opening), and this is also repaired at the same surgery. Post-operatively, it is of utmost importance to maintain a low-fiber diet and avoid constipation, straining, and large bowel movements. A special diet will be provided for our patients prior to discharge from the hospital.
